Financial Goals
Setting financial goals is also essential for achieving long-term financial stability and, in fact, financial freedom.

What are financial goals?
Whether your goal is to save for a down payment on a home, pay off debt, or build an emergency fund, having a clear objective in mind can help you stay motivated and focused. It can also help you make smarter financial decisions, such as choosing to invest in a retirement account rather than buying something that you don’t need.

Be smart and set smart goals
When setting financial goals, it’s important to make them specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
For example, rather than saying, “I want to save money,” you might set a goal to save Rs. 50,000 over the next 12 months. By setting specific targets and deadlines, you can track your progress and make adjustments as needed.
Classification of financial goals
Once a list of various goals is prepared, they need to be classified in terms of two criteria: time to goal and importance of the goal.
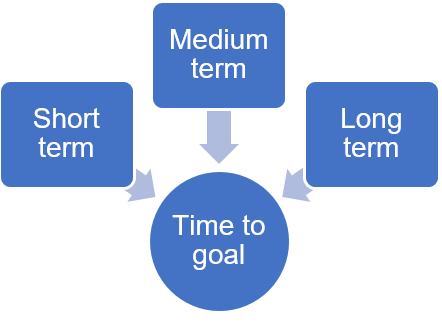
1. Time to goal: First of all, the goals must be segregated into immediate, short-term, medium-term, and long-term goals, depending on how far in the future they are.
2. Importance of the goal: Like we saw in the needs, wants, and desires, the financial goals can be categorized into critical needs, good-to-have goals, and dreams. There are no rules that one can set about how to assign importance to financial goals. For example, some may consider getting the kids educated the most important goal, whereas someone else may consider one’s retirement the primary goal.
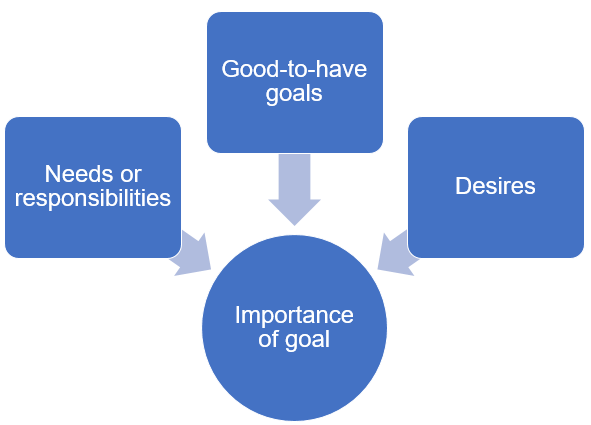
Once the goals are categorized using the above two criteria, one can understand the priority of each one. Investments and savings must be linked to the goals in terms of the priority thus arrived at. Please remember that the prioritization of financial goals will differ from person-to-person and from family-to-family.


