Managing your Income and Expenses

In the management of personal finances, the first step is budgeting (read the article on budgeting). Budgeting begins with taking stock of one’s income and expenses. After all, savings result from the difference between income and expenses. In other words, after accounting for the regular, necessary expenses, one is able to save out of one’s income. In such a case, both the income and expenses must be understood.
Two types of income
The income we earn from various sources can be categorized into two types:
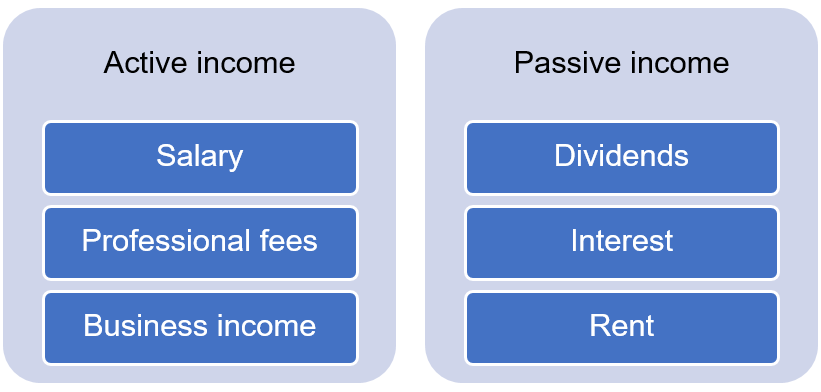
1. Active income
2. Passive income
Active income is what one gets by working and deploying their time and skills. It accrues as long as one works. On the other hand, the income from investments, for example, keeps accruing even when one takes a break or even in retirement. Basically, passive income is one that one earns without putting in any (or very minimal) physical or intellectual efforts.
There are largely two different types of expenses:

Two Types of Expenses
1.Mandatory or non-discretionary expenses
2.Discretionary expenses
There are certain mandatory expenses that every family must incur. These are largely pertaining to basic needs, whereas the discretionary expenses relate to wants and desires. (Read the article Understanding Needs, Wants, and Desires).
Passive income comes from investments, which come from savings. Savings can be increased through a reduction in expenses, where one can only control the discretionary expenses and not the mandatory ones.

Managing your income and expenses takes time and effort, but it’s worth it in the long run. By creating a budget, prioritising your expenses, cutting unnecessary expenses, saving for emergencies, and investing for the future, you can achieve your financial goals and live a more secure and comfortable life.
Let us look at a step-by-step approach to achieving the above balance:
1. Create a budget. The first step in managing your income and expenses is to create a budget. This means making a list of all your income sources and expenses. Make sure to include all your monthly bills, such as rent or home loan EMIs, utilities, food, transportation, premium payments for insurance policies, and any debt payments. Then, subtract your expenses from your income to see how much money you have left over.
2. Prioritize your expenses: Once you have a budget, you need to prioritize your expenses. Make sure you cover your basic needs first, such as food, shelter, and utilities. Then, focus on paying off any debt you have, such as credit cards or loans. After that, you can think about your other expenses, such as entertainment or travel.
3. Cut unnecessary expenses: Take a close look at your budget and see if there are any expenses you can cut. This could include eating out less, cutting down on costly loans to reduce the interest burden, or finding ways to reduce your utility bills.
4. Save for emergencies: It’s important to have an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses, such as medical bills. Emergency funds are also essential to cover regular household expenses in the event of a temporary loss of income, which could arise due to a loss of job, shutting down the business, or even poor health.
Aim to save at least three to six months’ worth of living expenses in an emergency fund.

5. Invest for the future: Once you have your budget under control and an emergency fund in place, you can start thinking about investing for the future, i.e., investing for medium- and long-term financial goals. Such money could be invested in securities like stocks and bonds, either directly or through investment vehicles like mutual funds.


