What is securities market?

Investors need to invest their money in line with their financial goals. They also need liquidity to be able to exit the investments. Securities markets provide a cost-efficient and reliable marketplace for investors to manage their investments.

Securities markets help household savings be effectively and efficiently channeled into productive investments like shares, debentures, precious metals (through gold and silver ETFs), and real estate (through REITs).
The functions of securities market
It is a marketplace for securities. While it offers an opportunity to investors to benefit from investing in securities issued by companies, governments, etc., it also offers liquidity or an exit route to existing investors of the same securities.
It is a marketplace for securities. While it offers an opportunity for investors to benefit from investing in securities issued by companies, governments, etc., it also offers liquidity or an exit route to existing investors in the same securities.
A well-regulated securities market instils faith among the investors and helps grow it further. Higher faith among investors draws more money from them in securities markets. Such a growth of the securities market is essential for the efficient allocation of resources within the economy. It enables household savings to go into nation-building while at the same time rewarding the investors, too
Segments within the securities market
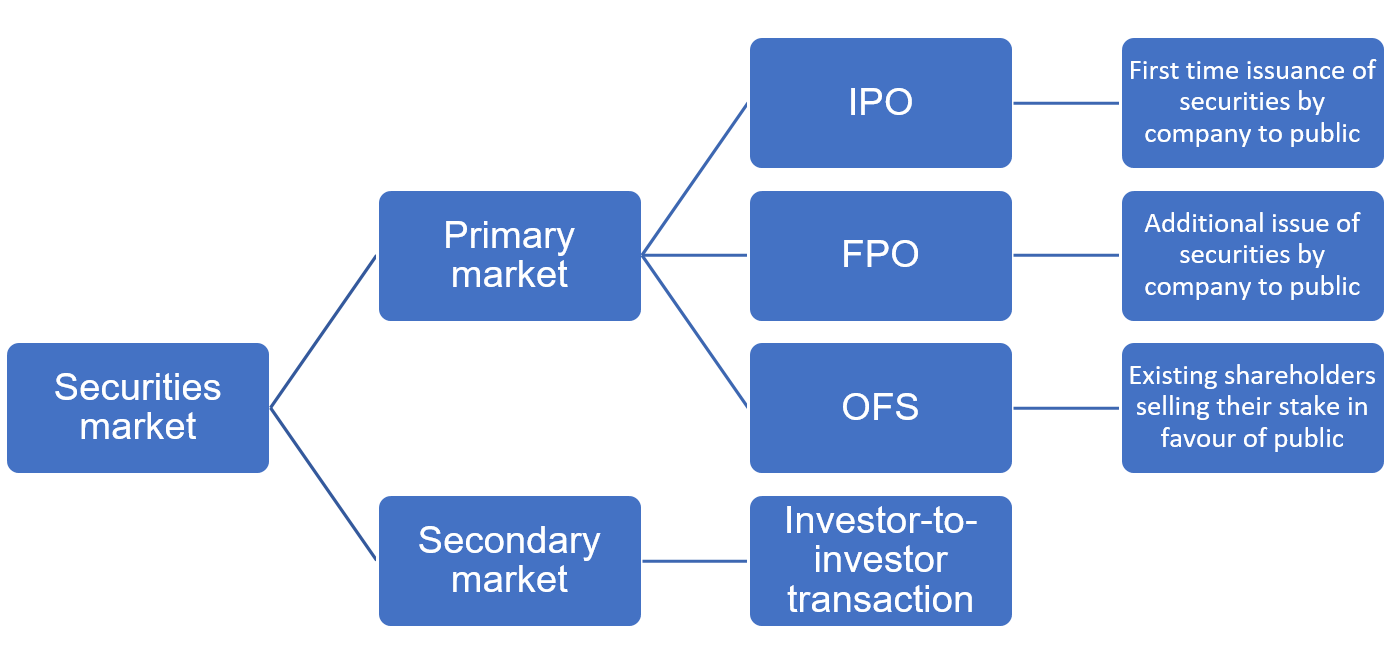
Securities markets have two distinct segments, known as the primary market and the secondary market
Primary market
One of the main objectives of the primary market is to allow companies to raise capital through the issuance of securities like shares and debentures. When a company raises money for the first time from the public through the primary market, the process is known as an initial public offering (IPO). If the company is raising funds again, the process is only slightly different and is known as the follow-on public offering (FPO).
Sometimes, a company could be operating as a private limited company with funding from promoters or even outside investors like venture capitalists and angel investors. When such investors offload the shares, allowing the public to subscribe to them, it is called an “offer for sale” (OFS).
In the case of both an IPO and an OFS, retail investors get the opportunity to invest in the shares of the company for the first time.
Secondary market
Once the shares are offered to the public through the primary market, they must be listed on a recognized stock exchange to offer liquidity to the investors who subscribed to the offer. This is the market where public shareholders can buy or sell their shares and is known as the “secondary market.
The secondary market offers an opportunity for investors to sell their shares to other buyers when they need money, when they spot another investible opportunity, or when they want to reduce their investment exposure to certain securities or certain types of securities.
Stringent disclosure and reporting requirements
The companies whose shares are listed on the stock exchanges have to follow stringent disclosure requirements as prescribed by SEBI and the stock exchanges from time to time, allowing the investors to take informed and timely decisions.
The combination of such timely and relevant disclosures along with the liquidity of the secondary markets work to enhance the safety of investor’s money.


