Understanding REITs
What are REITs?

Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) are pooled investment vehicles like mutual funds. However, the REITs, as the name suggests, invest in real estate. Thus, it is another way to invest in real estate through small investment sums. The units of REITs trade on stock exchanges at a price discovered through demand and supply.
Features of the REITs
The structure of the REIT is similar to that of a mutual fund in that there is a sponsor, a management company, and a trust. The trust owns the real estate properties on behalf of the beneficiary unit holders and is responsible for protecting their interests. The management company is vested with the responsibility for managing the real estate portfolio. Such a tripartite structure provides safety for investors.

The income for the REIT comes in the form of rental income from real estate investments as well as capital gains on the sale of such properties. The profit is derived after adjusting for various costs associated with the management of this real estate portfolio as well as the fees for various professionals, including the management company and the trustees.
Advantages of REITs
The real estate investment trusts provide simple solutions to some of the problems associated with physical real estate.
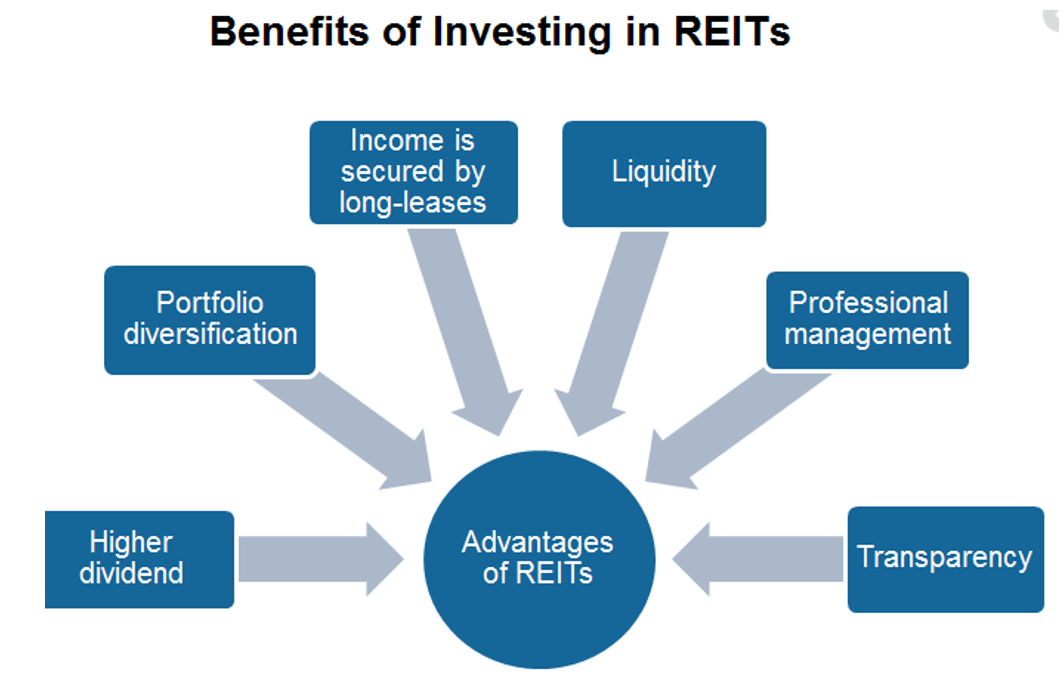
1. Low-ticket size: The investor can invest small amounts of money into the REITs.
2. Liquidity: As the units of REITs are listed on stock exchanges, there is reasonable liquidity (an exit option) for the existing investors. New investors can also invest at any point in time by buying these units on the secondary market without having to wait for a new launch.
3. Divisibility: A benefit related to liquidity and small ticket sizes is divisibility. In the case of physical real estate, when an investor wants liquidity, the entire property must be sold, as it cannot be divided into parts and sold off. REIT units can be sold on the exchange to the extent of the liquidity requirement.
4. Diversification: A typical real estate investment is done in a single property, or a couple of properties at most, in the majority of cases. This exposes the investor to the risk of a concentrated portfolio. REIT is a diversified portfolio across various different properties located across the country.
5. Transparency: The investor can easily know where the money is invested as well as what the fair value of the investment would be as the NAV is declared regularly.
6. Regulations: REITs are regulated by SEBI.

